Project Overview
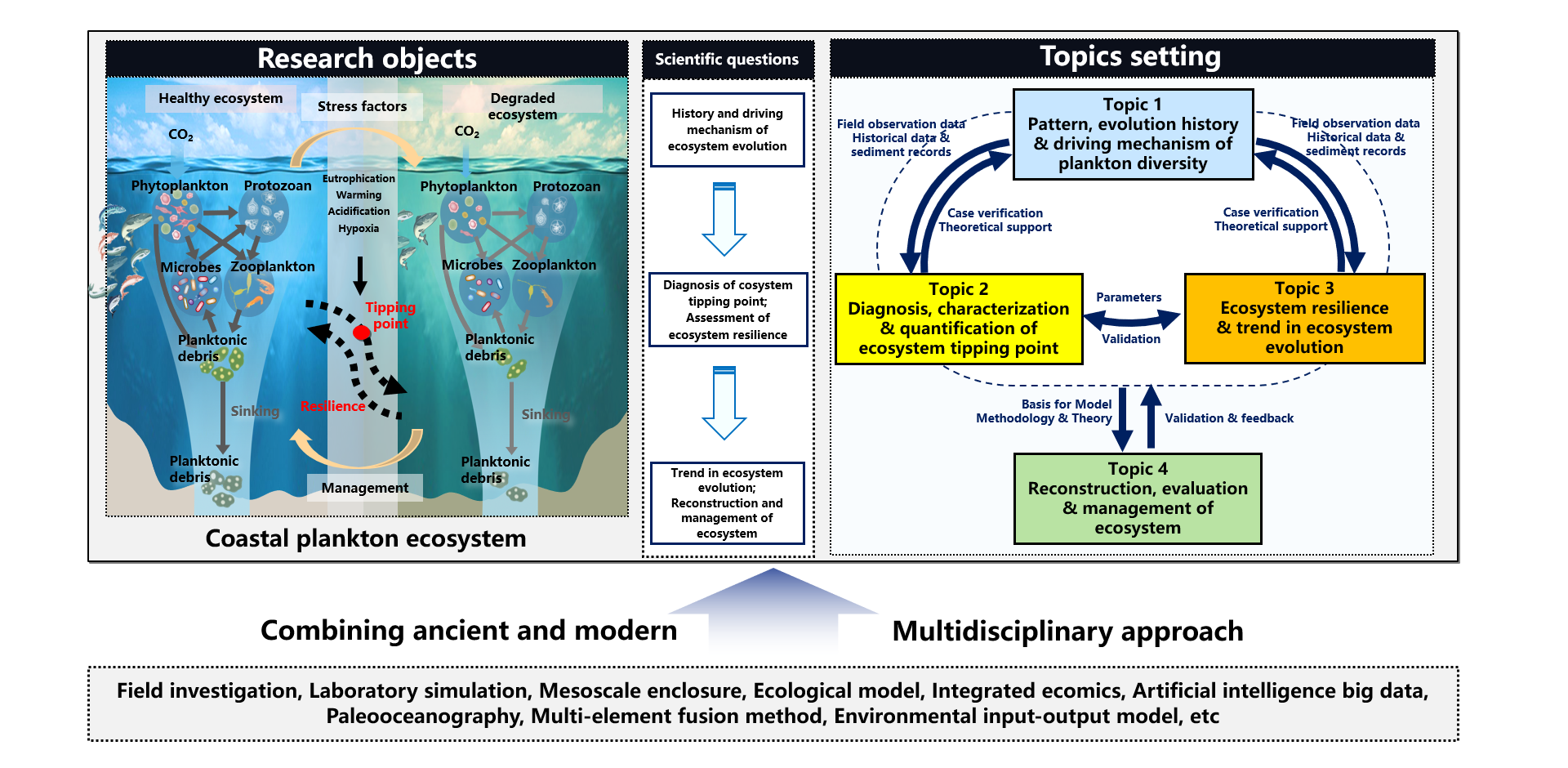
Planktonic ecosystems, composed of zooplankton, phytoplankton, microbe, and their living environments, are the cornerstone of marine ecosystem and regulators of marine carbon sequestration and storage, regulating the global environment and climate. Human activities and global changes have profoundly affected the planktonic ecosystem, including ocean acidification, warming, deoxygenation, and eutrophication, causing a decline in species diversity, weakened carbon sequestration and storage capacity, and a decline in service functions. This has led to a series of irreversible ecological and environmental effects, approaching tipping points and even causing transformation and reorganization of marine ecosystems, becoming one of the most prominent environmental problems in the world today.
This project was approved by The Administrative Center for China’s Agenda 21 on November 23, 2022. Xiamen University initiated the project, partnering with leading research institutes and universities, such as HKUST Fok Ying Tung Research Institute, Shandong University, China University of Geosciences (Wuhan), the Institute of Oceanology (CAS), South China Sea Institute of Oceanography (CAS), and Second Institute of Oceanography (MNR).
The core scientific question of this project is "tipping points, resilience and reconstruction of plankton ecosystem in typical marine areas under dual stresses of human activities and global changes". The plankton ecosystems in the Yangtze River Estuary, the Pearl River Estuary and adjacent waters that are significantly stressed by human activities and global changes, are selected as research areas. The tasks of this project includes: (i) integrate the existing pattern, historical data, sediment records of plankton diversity, and the system's steady-state transformation in different stress scenarios and extreme events; (ii) establish the theory and method of characterizing and quantifying the system's tipping points; (iii) evaluate the resilience and restoration ability under multiple environmental stresses; (iv) develop the theory and method of system reconstruction; (v) develop the prediction model of system evolution trend and realize the application demonstration of intelligent and situational prediction; (vi) put forward management strategies suitable for the coordinated development of China's offshore economy, human health and ecological environment; (vii) promote the scientific understanding of the tipping points, resilience and restoration ability of plankton ecosystem; (viii) clarify the evolution history, existing situation and driving mechanism of planktonic ecosystem under the dual stress of global change and human activities. This project will provide theoretical and methodological supports for formulating biodiversity conservation and climate change strategies, and implementing national strategies such as integrated land-sea management and carbon neutrality.
Principal investigator: Dazhi Wang (dzwang@xmu.edu.cn)
Project updates:
Official website of COASTAL-TREE


